Australian Dollar recovers from the intraday losses on upbeat Chinese data
- Australian Dollar recovers from the intraday losses on upbeat China's economic data.
- Australian Dollar receives pressure as the Aussie's per capita consumption decelerates.
- Governor Bullock mentioned taking responsive policy measures if inflation persists.
- US Retail Sales (MoM) surged by 0.7% in September, surpassing expectations of 0.3%.
The Australian Dollar (AUD) recovers from the intraday losses as China has reported unexpectedly positive data across various indicators. However, the AUD/USD pair halted its two-day winning streak earlier in the day. This shift followed a speech by Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) Governor Michele Bullock on Wednesday, coupled with upbeat economic data from the United States (US).
Australia's central bank expresses heightened concern about the inflation impact stemming from supply shocks. Governor Bullock stated that if inflation persists above projections, the RBA will take responsive policy measures. There is an observable deceleration in demand, and per capita consumption is on the decline.
Bullock mentioned that the full impact of previous rate increases on consumption has not materialized yet. In the face of persistent higher-than-anticipated inflation, the RBA acknowledges the necessity to act and emphasizes a cautious approach, remaining vigilant to potential upside inflation risks.
The US Dollar Index (DXY) attempts to recover from the previous losses, and this is attributed to the upbeat economic data from the United States (US). However, the dovish remarks from many Federal Reserve (Fed) officials suggest a cautious approach by the central bank, emphasizing a reluctance to tighten monetary policy in the current economic environment.
Richmond Fed President Thomas Barkin, noted that current policy is already restrictive. Barkin expressed uncertainty about the upcoming FOMC monetary policy meeting in November. He emphasized that the US central bank cannot depend on longer-term higher bond yields alone to tighten monetary conditions.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Australian Dollar weakens after the RBA Governor’s speech
- Australian Weekly ANZ Roy Morgan Consumer Confidence survey, released on Tuesday, indicates a decline in the nation's Consumer Confidence. The reading fell to 76.4 compared to the previous figure of 80.1. The decline is observed across all sub-indices, reflecting a more cautious or negative sentiment among consumers.
- RBA’s board members acknowledged in meeting minutes that there were significant concerns about upside risks to inflation. This suggests that the board is cautious about potential factors that could lead to an increase in inflation.
- China's Gross Domestic Product surpassed expectations, showing a growth of 1.3% compared to the anticipated 1.0%. The annual report for the same quarter revealed an increase of 4.9%, exceeding the expected 4.4%.
- Furthermore, China's Retail Sales (YoY) demonstrated a rise of 5.5%, surpassing both the previous figure of 4.6% and the expected 4.9%.
- RBA could introduce a central bank digital currency (CBDC). Brad Jones, Assistant Governor (Financial System) at the RBA, discussed the tokenization of assets and money in the digital era at The Australian Financial Review Cryptocurrency Summit.
- The ongoing conflict in the Middle East introduces an additional layer of complexity to the situation. This geopolitical factor could potentially prompt the RBA to implement a 25 basis points (bps) interest rate hike, reaching 4.35% by the end of the year.
- The US Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) disclosed that Retail Sales exceeded expectations of 0.3% MoM, which increased to 0.7% in September. While Retail Sales Control Group rose by 0.6% compared to the previous hike of 0.2%.
- This robust performance underscores the resilience of consumers. Subsequently, the Federal Reserve reported that Industrial Production showed improvement by 0.3%, which was expected to remain at 0.0%.
- Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia President Patrick Harker stated on Monday that the central bank should avoid creating new pressures in the economy by increasing the cost of borrowing. Harker further expressed the view that in the absence of a significant shift in the data, the Fed should maintain interest rates at their current levels.
- Investors appear to be exercising caution in making aggressive bets on the US Dollar (USD), given the uncertainty surrounding the Fed policy rate trajectory. The lack of a clear direction from the Fed on interest rates is influencing market sentiment and contributing to hesitancy among investors.
- The recovery in US Treasury yields from recent losses is seen as a potential factor that could provide support to the US Dollar. The 10-year US Treasury bond yield stands at 4.83%, by the press time.
- Additionally, the USD continues to benefit from safe-haven flows amid rising geopolitical tensions between Israel and Palestine. Safe-haven currencies, including the US Dollar, tend to attract demand during periods of heightened uncertainty and geopolitical risks.
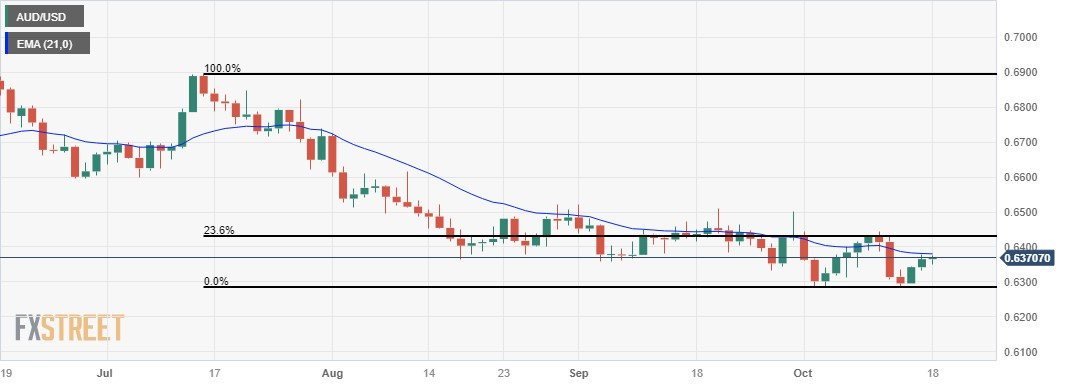
Technical Analysis: Australian Dollar hovers above the 0.6350 major level
The Australian Dollar trades around the major level of 0.6350 during the Asian session on Wednesday. The 0.6300 emerges as the significant support level, which aligns with the monthly low at 0.6285. On the upside, a crucial resistance is observed at the 21-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) around the 0.6379 level aligned to the major level of 0.6400. A break above the level could reach the region around the 23.6% Fibonacci retracement level at 0.6429. These technical indicators provide traders with insights into potential resistance zones that could influence the direction of the Australian Dollar.
AUD/USD: Daily Chart
Australian Dollar price today
The table below shows the percentage change of Australian Dollar (AUD) against listed major currencies today. The Australian Dollar was the weakest against the Japanese Yen.
| USD | EUR | GBP | CAD | AUD | JPY | NZD | CHF | |
| USD | 0.07% | 0.13% | 0.01% | 0.14% | -0.01% | 0.12% | 0.06% | |
| EUR | -0.08% | 0.04% | -0.08% | 0.06% | -0.09% | 0.03% | -0.03% | |
| GBP | -0.14% | -0.04% | -0.10% | 0.03% | -0.14% | -0.01% | -0.07% | |
| CAD | -0.02% | 0.07% | 0.10% | 0.11% | -0.03% | 0.11% | 0.04% | |
| AUD | -0.16% | -0.09% | -0.03% | -0.14% | -0.18% | -0.04% | -0.10% | |
| JPY | 0.01% | 0.09% | 0.15% | 0.04% | 0.19% | 0.11% | 0.07% | |
| NZD | -0.13% | -0.04% | 0.00% | -0.10% | 0.02% | -0.13% | -0.07% | |
| CHF | -0.05% | 0.03% | 0.08% | -0.04% | 0.10% | -0.07% | 0.08% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the Japanese Yen, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/JPY (quote).
Australian Dollar FAQs
One of the most significant factors for the Australian Dollar (AUD) is the level of interest rates set by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA). Because Australia is a resource-rich country another key driver is the price of its biggest export, Iron Ore. The health of the Chinese economy, its largest trading partner, is a factor, as well as inflation in Australia, its growth rate and Trade Balance. Market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – is also a factor, with risk-on positive for AUD.
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) influences the Australian Dollar (AUD) by setting the level of interest rates that Australian banks can lend to each other. This influences the level of interest rates in the economy as a whole. The main goal of the RBA is to maintain a stable inflation rate of 2-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively high interest rates compared to other major central banks support the AUD, and the opposite for relatively low. The RBA can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former AUD-negative and the latter AUD-positive.
China is Australia’s largest trading partner so the health of the Chinese economy is a major influence on the value of the Australian Dollar (AUD). When the Chinese economy is doing well it purchases more raw materials, goods and services from Australia, lifting demand for the AUD, and pushing up its value. The opposite is the case when the Chinese economy is not growing as fast as expected. Positive or negative surprises in Chinese growth data, therefore, often have a direct impact on the Australian Dollar and its pairs.
Iron Ore is Australia’s largest export, accounting for $118 billion a year according to data from 2021, with China as its primary destination. The price of Iron Ore, therefore, can be a driver of the Australian Dollar. Generally, if the price of Iron Ore rises, AUD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Iron Ore falls. Higher Iron Ore prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance for Australia, which is also positive of the AUD.
The Trade Balance, which is the difference between what a country earns from its exports versus what it pays for its imports, is another factor that can influence the value of the Australian Dollar. If Australia produces highly sought after exports, then its currency will gain in value purely from the surplus demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase its exports versus what it spends to purchase imports. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens the AUD, with the opposite effect if the Trade Balance is negative.

Comments are closed.